

國立臺灣海洋大學教育研究所碩士班
廖雅盈
國立臺灣海洋教育中心主任 張正杰副教授
![]()
壹、前言
海洋經過長期的演化產生了豐富且多樣化的海洋生物,提供人類在食物、醫藥和海洋休閒等方面的需求,不僅如此而已,海洋中的綠藻更是大氣層氧氣的製造者,是人類所需氧氣的主要來源。臺灣海岸線總長度約 1,566 公里,西為臺灣海峽,東臨太平洋,南接巴士海峽,北面東海,配合著溫暖的黑潮與西南季風,和大陸沿岸的冷水團流經後,帶來了許多不同海洋生物。臺灣曾經擁有過豐富的海洋生態,卻在這短短的三、四十年裡由於各種人為的破壞,造成資源衰退、物種絕滅十分嚴重,全球暖化使得海水溫度上升,海洋的環境已經在改變。海洋生物學家Jeremy, Wolfgan, Karen, Louis, Bruce & Robert (2001)在Science期刊上曾提到,人類的過度捕撈是影響海洋生態最重要的原因。而生物多樣性之父,威爾森(E. O. Wilson)也不只一次提到,地球目前正面臨有史以來第六次的大滅絕,是唯一一次純粹由於人為因素所造成的大滅絕。同時,世界自然基金會(World Wide Fund for Nature,WWF)研究小組也曾發表研究調查於Science科學期刊,內容提及如果過度捕撈的問題再不解決,將導致全球2048年會無魚可吃,海洋生物多樣性也會悉數滅絕。2003年在義大利興起的一股慢魚運動旋風正在全球慢慢蔓延。
綜觀全球漁業產量都在迅速衰退,包括像是魚體的小型化和大型魚種越來越少…等等的現象,其原因大部分歸咎於過度捕撈與不永續的漁法捕撈造成環境生態的破壞。但,當我們深入去探究這件事情,就不難發現其實「過度捕撈」背後所隱藏的真正問題就是與我們的消費源頭有關係(圖1)。
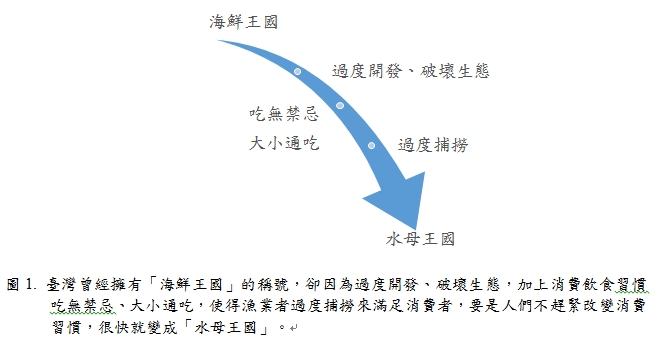
![]()
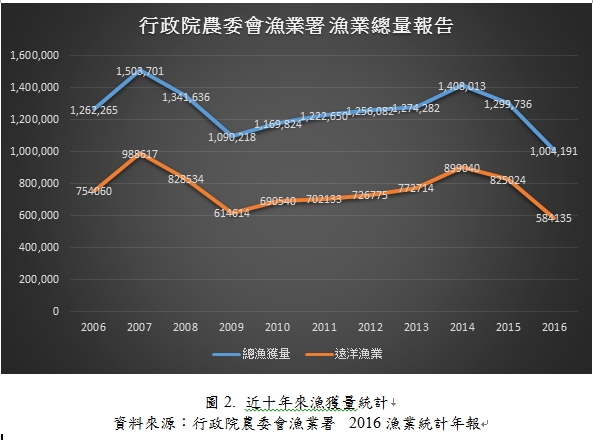
| 參、用消費行動來守護海洋 臺灣雖然四面環海,擁有生物的物種多,但並非表示臺灣的資源數量很豐富。根據行政院農委會漁業署2007年到2016年統計,臺灣每年的總漁貨量,從150萬噸已經下跌到100萬噸,而其中遠洋漁業產量也從98萬噸跌到58萬噸(圖2)。換言之,如果我們再不積極採取全民海鮮永續行動,我們的後代子孫將無海鮮可以享用。 |
李振華(2008)提到,對海洋漁業資源來說,消費對其產生極大的影響。人們的消費需求與海洋資源之間保持著均衡和協調是永續海洋資源的首要途徑。身為這個地球上的一份子,我們除了要呼籲政府丶監督政府推動一些限漁的措施、劃設海洋保護區和制訂漁業標章並落實管理取締的工作外,更重要的是我們每一位消費者也可以從自己買對魚和吃對且適量的魚來拯救海洋,做一個有海洋素養的地球公民,讓海洋可以恢復蓬勃的生命力,這是我們可以留給下一代子孫的財富。
![]()
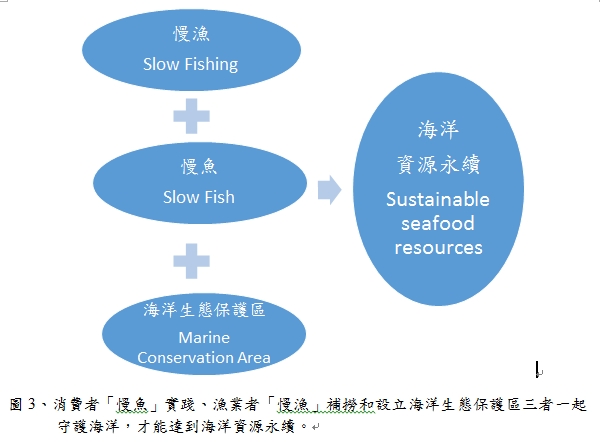
肆、從「慢魚」到「慢漁」
慢魚(Slow
Fish)運動起源於義大利,一開始的理念是來自以「慢食」Slow
Food的概念為出發,為了要能讓每個人每天都能有美食的享受,並恢復人們長期以來與地球和與其食物的連結,鼓勵並建議人們可以從選擇Good、Clean、Fair
Fish的「慢魚」行動方式來實踐,透過消費者能有正確的海鮮選購認知來買對魚、吃當季且適量的魚(所謂的「適量的吃」是指能否讓海洋資源有足夠的時間恢復其再生力)。最後,透過消費者的行動來監督並影響上游的捕撈漁業可以秉持著尊重及友善環境的漁法來進行對適當體型及適當數量的魚類「慢漁」捕撈方式
(圖3) 來達到海洋資源永續。
伍、慢魚運動教學理論
隨著國人生活及消費習慣的改變加上對永續海洋資源的觀念不足,究竟站在守護海洋第一線的消費者該如何正確選購海鮮,來達到永續資源,拯救海洋呢!由臺灣永續鱻漁發展協會和台灣魚類資料庫所推出的各項選購海鮮原則提供給民眾在購買海鮮產品上的參考和依據。
《永續食魚教育五要點》和《臺灣海鮮永續原則:3選3減3不》
「台灣永續鱻漁發展協會」於2017年9月17日成立大會,並在2018年通過內政部核可,其協會宗旨為保護環境、尊重生命、永續海鮮、海洋永續。發起人白尚儒更提出《永續食魚教育五要點》和《臺灣海鮮永續原則:3選3減3不》盼以食魚教育來帶動永續漁業(臺灣永續鱻漁發展協會,2017)。
《永續食魚教育五要點》
一、物種認識/名字、特徵、生態習性
二、生產介紹/如何被捕撈或養殖的?
三、處理烹調/屠宰分解、料理烹調
四、選購嚐鮮/挑選要訣、採買時節和挑骨刺
五、人文風俗/該物產所衍伸出的習俗文化
《臺灣海鮮永續原則:3選3減3不》
一、選擇非繁殖巔峰期間的海鮮,少食用以精卵為主打的野生海鮮。
二、選擇捕撈對環境較友善的漁法,或資源符合永續管理的海鮮。
三、選擇成長快、換肉率高、對環境負擔小、對動物性蛋白質需求低的養殖品種。
四、減少食用野生捕撈的幼魚與老成魚,應選擇成魚食用。
五、減少食用由臺灣野生海鮮加工而成的長效保存食品。
六、減少食用大型種,以小型種為首選、中型種其次,少食用長壽與資源恢復速度慢的種類。
七、不購買有動保爭議或資源瀕危的品種。
八、不購買臺灣有相似產品,價錢卻更便宜的進口海鮮。
九、不購買魚身有斑點或蠕型花紋,且同時可清楚辨識出黃、綠、藍、白兩種以上顏色組合的小型魚。
《臺灣海鮮選擇指南》
《臺灣海鮮選擇指南》為中央研究院生物多樣性研究中心邵廣昭教授和廖運志博士等人所製作,提供給消費者在選購海鮮時可以參考。手冊裡將一般較常看到的水產品分為三類:「建議實用」(綠色)、「想清楚」(黃色)、「避免食用」(紅色),並建議在購買海鮮前依循下面幾點原則來做選購:
一、常見種(量多) > 稀有種
二、銀白色 > 有色彩
三、迴游種 > 定棲種(前者種類少、數量多)
四、沙泥棲地 > 岩礁棲地(後者種類多、數量少)
五、不買遠道而來的海鮮(耗能)
六、不買長壽的大型掠食魚(汞等重金屬量高)
七、養殖魚 > 海洋捕撈魚 (野生魚類已經越來越少)
八、不買養殖的蝦、鮭、鮪(其餌料為魚粉或下雜魚)
九、購買養殖的吳郭魚、虱目魚等(其餌料為植物性餌料)
十、購買食物鏈底層的海鮮—底食原則
十一、不買非使用永續漁法撈捕的漁獲
可參考底下網站:http://fishdb.sinica.edu.tw/chi/seafoodguide.php
選擇常見種類且數量足夠的魚類,像是白帶魚及飛魚捕撈方式較不會破壞海底生態因為棲息於中表水層的洄游魚類,但仍須注意捕撈的量是否能讓其恢復再生力;岩礁棲地的魚類物種雖多,但數量少且資源恢復較不易,捕撈時也會破壞到岩礁生態故應避免;長壽的大型掠食魚生長週期長加上因位於生態食物金字塔的頂端,汞等重金屬累積的量高,應避免食用;野生魚類目前已經因為過度捕撈、棲地破壞等等問題,數量已經不比從前,因此建議選擇餵食植物性餌料的養殖魚類。建議消費者在購海鮮時,依循前面幾點原則,並要拒絕購買使用對環境不友善漁法捕撈的漁獲(廖運志、邵廣昭,2016)。
陸、慢魚運動教學內容
臺灣社會結構面臨少子化,家庭飲食文化都過於遷就孩子,不是獨生子女,就是隔代教養,吃的問題都是以孩子為中心,雖然孩子不是直接的消費者,但卻是背後的飲食消費決定權者。透過以下的慢魚運動教學內容的設計(圖4),讓孩童除了可以有正確的選擇海鮮觀念,並可以培養孩童永續海洋資源的態度,他們是未來的主人翁,透過孩童來進而影響家庭成員,他們的選擇是可以對地球、對海洋有很深的影響,以達到守護海洋、永續海洋資源。
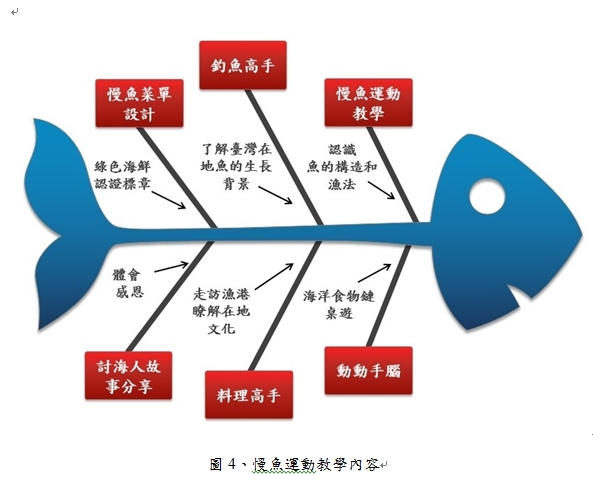
(1)
慢魚運動教學:可依據不同年齡層的孩童設計簡報,藉以讓學生瞭解魚的構造及認識和討論各種漁法對海洋生態所造成的影響。
(2)
動動手腦:設計海洋食物鏈桌遊,透過遊戲式學習讓學生瞭解大海裡的食物鏈,每種生物的生態圈和另外一個生物的生態圈是環環相扣、相互制衡的,可參考《海洋教育:認識海洋的教與學》一書。
(3)
釣魚高手:布置教室學習角,並設計海洋生物教材,透過情境式學習認識台灣在地魚類及其生長背景,可參考《海洋教育:認識海洋的教與學》一書。
(4)
慢魚菜單設計:學生可以依照上述提及的《永續食魚五要點》、《臺灣海鮮永續原則:3選3減3不》和《臺灣海鮮指南》設計出一道屬於自己的慢魚菜單(圖5)
(5)
海洋工作相關人士來分享:邀請具有在海上工作經驗的人士來和學生分享在海上航行或捕魚過程中的小故事,讓學生可以體會到討海人的辛苦,面對大自然應該要懷著感恩的心。
(6) 認識漁港/料理高手:
帶學生走進漁市場感受在地家鄉文化,學習運用較不破壞食材鮮味的料理方法來烹調每一道大海賜予給我們的美食。

陸、結語
面對現在全球海洋資源漸漸枯竭,透過慢魚運動教育推廣來喚起全民海洋素養,在傳遞正確的選擇海鮮認知給我們的下一代時,除了應保有一顆感恩的心來品嚐大自然所賜與的美食,還要讓他們知道,他們的選擇是可以對地球、對海洋有幫助、有影響,每一個消費者可以從買對魚和吃對且適量的魚來拯救海洋。
消費者選對魚、漁業者補對魚,才會年年有魚!
![]()
柒、參考文獻:
1.
白尚儒(2017)。《永續食魚教育五要點》,基隆,臺灣:臺灣永續鱻漁發展協會。
2.
李振華(2008)。消費結構變化對海洋漁業資源環境的影響分析-以浙江為例。漁業經濟研究6,17-21。
3.
邵廣昭、廖運志(2015)。《臺灣海鮮選擇指南》,臺北,臺灣:臺灣魚類資料庫。
4.
廖運志、邵廣昭(2016)從臺灣海鮮選擇指南看消費者行動。臺灣博物季刊 35(2): 26-35。
5.
羅綸新、黃明惠、張正杰(2012)《海洋教育:認識海洋的教與學》。台北,臺灣:高等教育。
6. Jeremy J.,
Michael K., Wolfgan H. B., Karen A. B., Louis W. B., Bruce J.
B., ...Robert R. W. (2001). Historical overfishing and the
recent collapse of coastal ecosystems. Science, 293(27),
629-637.
7. Slow Food(2015). Slow Fish Retrieved from
http://slowfood.com/slowfish/
![]() From Slow
Fish to Slow Fishing, Saving the Ocean by Consuming the Correct
Seafood
From Slow
Fish to Slow Fishing, Saving the Ocean by Consuming the Correct
Seafood
Institute of Education, National Taiwan
Ocean University
Y.I., Liao
Dr. C.C., Chang
Translated by
Translated by Kaifu Chang
Preface
After a long-term evolution, the ocean has made rich and
various marine life come into existence which fulfill people’s
needs of food, medicine or ocean recreation. In addition to
that, the green algae are the main manufacturers of the oxygen
in the atmosphere, the main source of the oxygen human beings
need.
The coast line of
Taiwan has reached 1,566 KM. With Taiwan Strait in the west, the
Pacific Ocean in the east, Bashi Channel in the south and East
China Sea in the north, accompanied with warm Kuroshio Current
and west-southern monsoon and cold-water mass from continental
coastline, numerous marine life has therefore been brought here.
Taiwan used to have abundant marine biology. For the past four decades, the
resources and species have decreased to a severe extent. Global
warming has made the water temperature rise and changed the
marine environment. Wolfgan, Karen, Louis, Bruce & Robert
(2001) stated that overfishing was a critical
influence on marine biology. E. O. Wilson has repeatedly
mentioned that human beings are facing the sixth extinction
whose cause was mainly because of human being ourselves.
Meanwhile, World Wide Fund for Nature also indicated that if overfishing is
not to be solved, there will be no fish by 2048. The marine life
will be totally extinct. As a result, a movement named Slow Fish
started to broadcast from Italy.
An overview of
global fishery, people can find rapid regression like downsizing
of fish, decrease of large fish etc. The reason may be
overfishing and the environmental biology damage caused by
non-sustainable fishing. However, once we start to examine the
situation seriously. We can easily find the ways of our
consuming have to take the blame.
The Myth of
Seafood Consumption in Taiwan
Surrounded by the seas
and the used-to–be abundant marine diversity which led up to 1.2
million tons of fishery production annually, Taiwan was once
known as the Seafood Kingdom. Because of the fishing boat Shuen
De Ching No.888 incident, Taiwan was listed on the illegal,
unreported and unregulated fishing countries by EU. EU has been
warning Taiwan for nearly 2 years. In addition to that, people’s
desires of making coral reef fish the delicacies on the table
never quench.
Bread is the staff
of life. Especially when it comes to seafood which contains
many nutrients for human health like EPA
(Eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid)found in oil of
different fish. These nutrients are beneficial to reduce
inflammation, lower cholesterol and supplement calcium. We can
therefore know that human growth and body adjustment are deeply
related to seafood which has made it an important role on our
dining table.
As the rising necessities
of seafood, many high-tech fishing boats and fishing methods
have come to exist to measure up the fishery expectations. On
the other hand, the governments have been eager to promote
fisher village prosperity and to take care of fishermen’s
livings. They brainstormed to draw people’s attention to buying
and eating seafood by holding kinds of seafood season
activities. These activities seemed to be popular but neglected
the everlasting development of seafood.
When the seafood fever is cool down, the extinction comes after
because of our consuming too much seafood. We forgot that
restoring these marine resources takes time. Only knowing the
correct ways to consume proper amount of seasonal seafood can we
make our marine resources everlasting.
Guarding Ocean by Consuming
Actions
Although surrounded by the ocean and biodiversity, it doesn’t guarantee
that Taiwan has abundant resources. According to Fishery Agency,
Council of Agriculture Taiwan, the total number of fishery
production has decreased by half million tons comparing 2007 to
2016. Deep sea
fisheries have reduced to 580,000 tons. In other words, if we
are not to take positive actions, our future generation will no
longer have seafood.
Li (2008)
indicated that consuming has a great influence on fishery
resources. A concord balance between human consuming and marine
resources is the first strategy of everlasting marine resources
development. As global villagers, we should appeal to our
government for concentrating on marine related issues such as
fishing limit, marine conservation area establishment as well as
fishery management.
Furthermore, we can start from ourselves by eating proper amount
seasonal seafood and being marine-literacy citizens to make the
ocean recover its vitality leaving the marine riches for our
next generations.
From Slow Fish to
Slow Fishing
Slow Fish movement started from Italy whose concept was
originated from Slow Food to make people enjoy delicacies every
day and reconnect the links among the earth, food and human
being ourselves. People are suggested to choose good, clean,
fair fish. Consumers are taught to buy and eat fish with right
marine literacy. And hopefully, through consumers’ influences,
the fishery industry can adopt environmental-friendly fishing
methods to catch fish and make seafood resources sustainable.
Teaching Theories of Slow Fish
Because of the
changing consuming habits and insufficient concepts toward
everlasting marine resources, Sustainable Seafood and Fishery
Development Association and The Fish Database of Taiwan have
indicated several guidelines for people to refer when buying
seafood.
Sustainable Seafood and Fishery
Development Association was formed in 2017 whose targets are to
protect the environment, respect living creatures, maintain
sustainable seafood and make the ocean everlasting.
Five Points of Sustainable Seafood Education
Species
Recognizing: names, characteristics and biological behavior
Production Procedures: wild capture or aquaculture
Cooking:
butchering and cooking
Ways of Selection: tips and seasonal
purchasing
Humane culture: related culture origins
Principles of Taiwan
Sustainable Seafood: Choosing, Reducing and Refusing
Choosing seafood which are not in their breeding season
Choosing seafood caught from environmental-friendly fishery
methods or sustainable resources
Choosing fast-growing, high feed-conversion-rate,
less environmental burden, low requirement of animal protein
aquaculture breeds
Reducing eating wild caught juvenile but
marketing fish
Reducing eating preserved food made from wild
caught Taiwan seafood
Reducing eating neither large but small
or medium species nor long life-expectancy or slow-recovering
ones
Refusing to buy controversial wild conservation or
near-extinction species
Refusing to buy relative cheaper
imported seafood
Refusing to buy those small fish with spots
or stripes and can be distinguished with at least 2 colors
combination such as yellow, green, blue and white
Guidelines of Taiwan Seafood Selection
Guidelines of
Taiwan Seafood Selection were proposed by Prof. Shao, and Dr.
Liao for people to refer when buying seafood.
In this manual,
the marine products were categorized into three colors, green
which stands for recommendation, yellow for caution and red for
avoidance. Here are some also some tips before purchasing.
Common rather than
rare fish
Silver white than colorful
Migration than
residential habitation
Sand habitats than reef ones
No
distant seafood
No long-life large predatory fish
Aquaculture than wild catching
No aquaculture shrimps, salmon
and tuna
Buying aquaculture tilapia, milkfish etc.
Buying
seafood from the lower level of food chain
No seafood from
non-sustainable fishery methods
Referring website:http://fishdb.sinica.edu.tw/chi/seafoodguide.php
Choosing
common and sufficient fish such as largehead hairtail
(Trichiurus lepturus) and sailfin flying-fish is less harmful to
marine biology because they are migration fish that inhabit in
mid-surface level of waters. But we still have to be careful
with overfishing which may hinder its reproducing. Reef fish is
numerous but small in amount and hard to increase population in
a short time. Also, when fishing, the reef may be damaged,
therefore we should avoid this sort of fish. Long-life predatory
fish ranked at the top of the food chain also should be avoided
for its high accumulation of mercury. Wild fish population has
been diminishing because of overfishing, habitats destruction
and so forth. Thus, aquaculture fish fed on plant food is
suggested.
Based on these mentioned guidelines,
consumers are recommended not to buy seafood caught from
non-environmental-friendly fishery methods.
Contents of Slow
Fish Course
Nowadays,
Taiwanese families are under the influence of sub-replacement
fertility which may imply that more attention is shifted to
younger generation. They may seem to be children. Instead, they
are actually the key people to food consuming.
Through the Slow
Fish Courses, children can cultivate the correct concepts of
choosing seafood and the attitudes of sustainable marine
resources. They are the future pillars of our society. What they
choose may post critical influence on the earth and the ocean.
We hope that by educating the youth can their family member be
potentially moved to protect and sustain the marine sources.
Slow Fish: using
PowerPoint files to let students know the fish structure and
discuss the impacts of different fishery methods
Brainstorming: making a board game of marine food chains,
through games, students can understand one marine food chain can
connect as well as check and balance another
Fishing Experts:
decorating classroom with marine life, students can know the
background of local fish
Slow Fish Menu Designing: students
can design their own menu according to the guidelines mentioned
before
Marine Talk: inviting people who work in
marine-related fields give speeches to students
Knowing Fish
Harbors: taking a fieldtrip to the fish market to experience
local community culture, learning a better way to cook the food
given from the ocean
Conclusion
Facing the depleting marine resources, we are now trying to
arouse people’s marine literacy by Slow Fish Movement. On the
other hand, we are also conveying correct seafood choices to our
next generation with a blessed heart to enjoy the food given by
nature. Moreover, their choices can be helpful for the earth and
the ocean. Every consumer can save the ocean by buying and
eating the proper fish.